Further insights into the detailed process steps can be found in our download area
You can use the form to request access data for the download area.
To the download area

In the DIAMOND project, a Common Data Model that can be adapted to different use cases and a modern data exchange via common data spaces are being developed and tested. In addition to technical solutions, the organizations and needs of involved persons of the companies are also considered. The focus of the project, which is funded by the EU and the federal government and has 25 consortium partners. It is on the process of production plant planning and design in the automotive industry.
Blueprint processes and strategies for the migration to the digital twin in the complete plant design process.
Increased transparency and resilience of production facilities through comprehensively networked value creation processes.
Complete control over the entire vehicle life cycle through the digital twin.
Future planning services Made in Germany
Dissemination and utilization of project results in the vehicle and supplier industry.
Data integrity and availability despite complex processes through loss-free and efficient data processing.
To achieve data consistency in the heterogeneous tool landscape of the digital plant design process, consistent standards must be applied to data structures and data exchange technologies.
Neutral and scalable data models that can be mapped using standardized data exchange technologies enable a high level of market penetration, which ultimately leads to a significant acceleration of processes along the entire value chain in the plant design process.
A neutral and digital Common Data Model for individual machines, production resources and components, but also for products and processes, will form the basis for the digital plant creation process from initial planning to commissioning of the production plant and will be used to derive standards and interfaces in the form of demonstrators.

Thanks to its standardized structure, the Common Data Model enables a uniform exchange of data and information between different systems and software applications. This facilitates collaboration between automotive manufacturers and their suppliers, as the data is uniform and easy to understand. As a result, collaboration can be made more efficient and productive.


Through its standardized structure, the Common Data Model enables a structured exchange of data and information along the plant manufacturing process between automotive manufacturers and their suppliers, regardless of the software used. This facilitates collaboration and enables data and information to be exchanged more quickly and accurately, improving the efficiency and quality of the plant manufacturing process.

Thanks to its standardized structure, the Common Data Model enables a fast and efficient exchange of data and information along the plant manufacturing process between automotive manufacturers and their suppliers. This can help to shorten project times in the development of production plants, as the data is available in a standardized form and can be processed more quickly. This can speed up the integration of new vehicles and drive technologies, which can increase the company's adaptability and competitiveness.
Through its standardized structure, the Common Data Model enables a uniform and cross-company exchange of data and information, regardless of the software used. This can significantly improve data exchange for both new and reused production equipment, as data is available in a uniform state and can be exchanged faster and more accurately. This can increase collaboration and the efficiency of the plant manufacturing process.
Here you get insights into the current results of the research project DIAMOND
07.08.2023
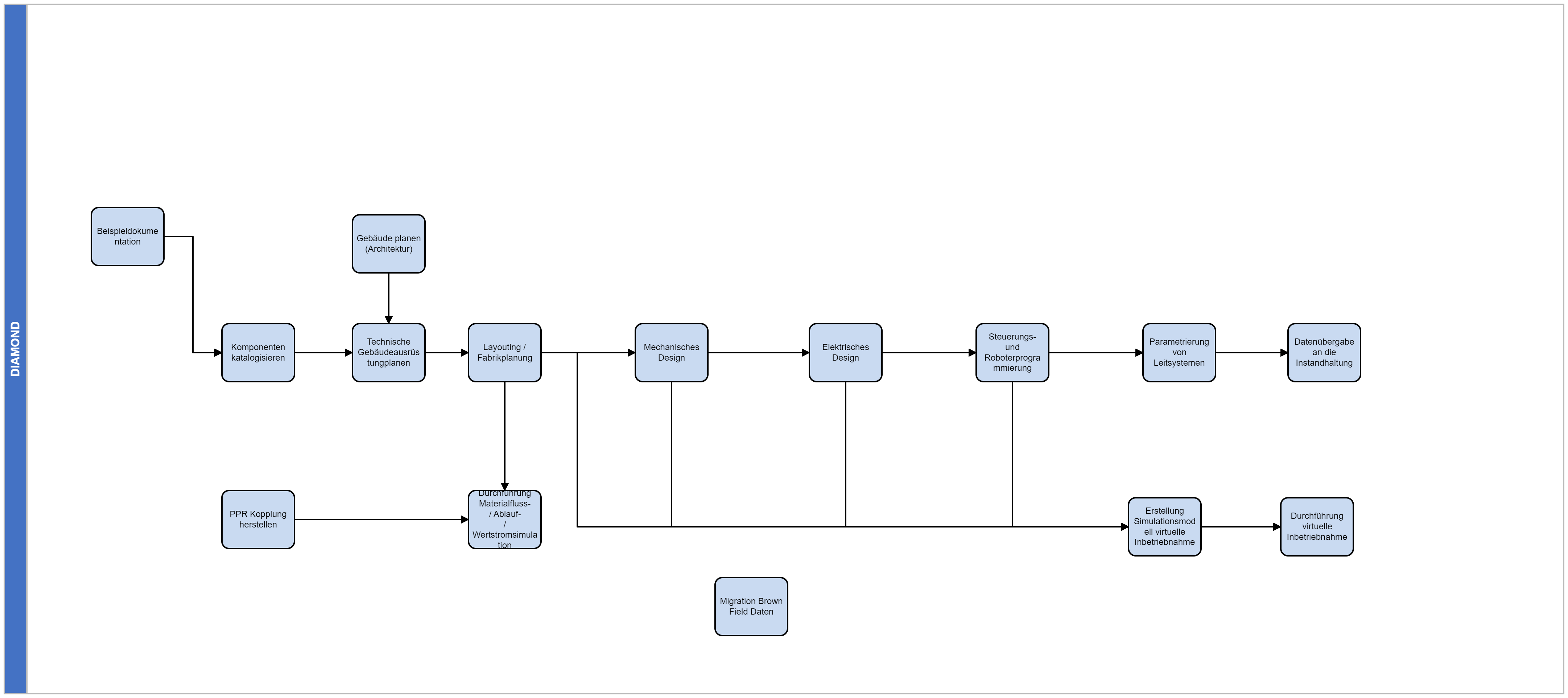
An analysis of the involved process steps and the resulting data flow
Content can only be displayed if cookies are accepted.
The federal government has allocated a multi-billion amount in the economic stimulus package to address the structural changes in the automotive industry, aiming to initiate a sustainable, rapid, and technology-neutral transformation within the sector.

You can use the form to request access data for the download area.